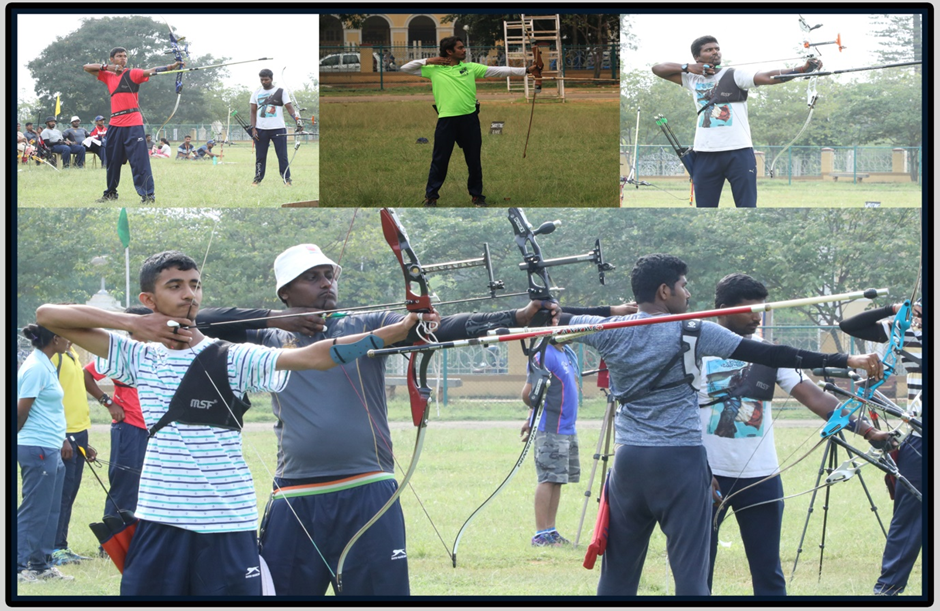

Archery is a skill of using bow and arrows to shoot. This word Archery comes from the Latin arcus which means "BOW" or "ARCH". Historically, Archery was used for hunting adn combat. A person who participates in archery is typically called an archer or a bowman. It is mainly a competitive sport and recreational activity.
Bows and arrows have been present in Egyptian culture since its predynastic origins. In the Levant, artifacts that could be arrow-shaft straighteners are known from the Natufian culture, (c. 10,800–8,300 BC) onwards. The Khiamian and PPN A shouldered Khiam-points may well be arrowheads. Bows and arrows have been present in Egyptian culture since its predynastic origins. In the Levant, artifacts that could be arrow-shaft straighteners are known from the Natufian culture, (c. 10,800–8,300 BC) onwards. The Khiamian and PPN A shouldered Khiam-points may well be arrowheads.
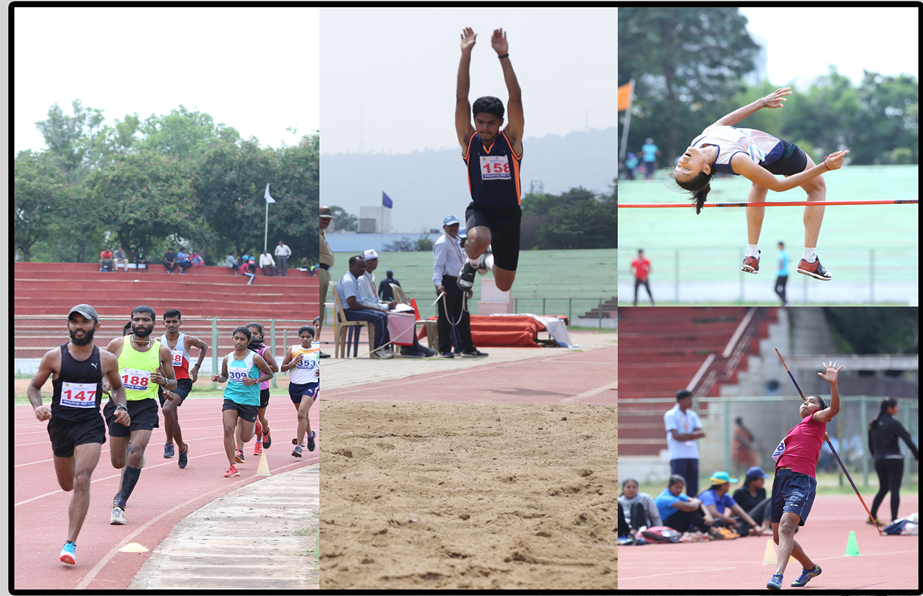

Athletics is a collection of sporting events that involve competitive running, jumping, throwing, and walking. The most common types of athletics competitions are track and field, road running, cross country running, and race walking. The results of racing events are decided by finishing position (or time, where measured), while the jumps and throws are won by the athlete that achieves the highest or furthest measurement from a series of attempts. Athletics is mostly an individual sport, with the exception of relay races and competitions which combine athlete's performances for a team score, such as cross country. The 100-metre dash is one of the most popular and prestigious events in the sport of athletics. The reigning 100 m Olympic champion is often named .the fastest runner in the world.. Athletics was included in the first modern Olympic Games in 1896 and it has been as one of the foremost competitions. Athletics was incorporated into the Asian Games in 1951.
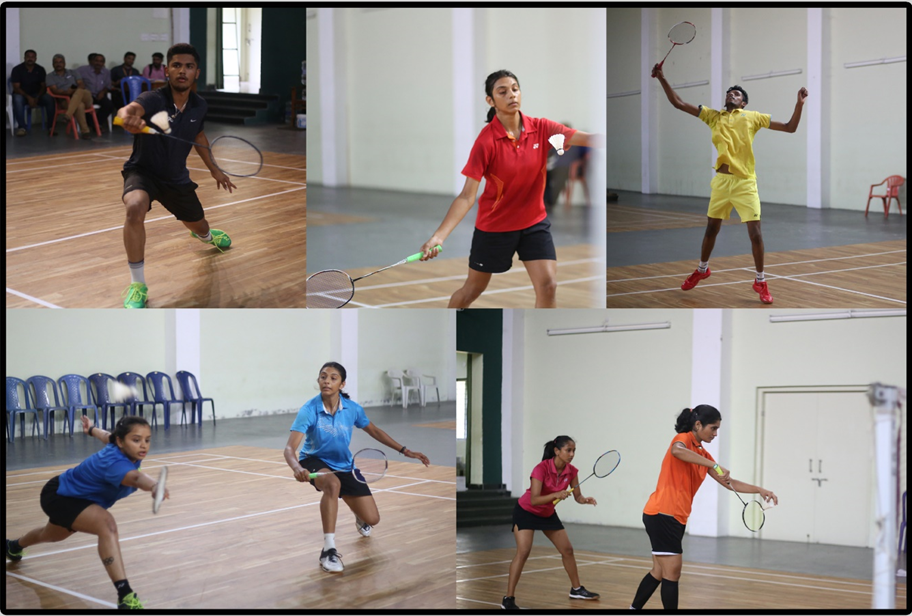

Badminton is a racquet sport played using racquets to hit a shuttlecock across a net. Badminton is often played as a casual outdoor activity in a yard or on a beach; formal games are played on a rectangular indoor court. Play ends once the shuttlecock has struck the floor or if a fault has been called by the umpire, service judge, or (in their absence) the opposing side.
The game developed in British India from the earlier game of battledore and shuttlecock. European play came to be dominated by Denmark but the game has became very popular in Asia, with recent competitions dominated by China. Since 1992, badminton has been a Summer Olympic sport with five events: men's singles, women's singles, men's doubles, women's doubles, and mixed doubles. At high levels of play, the sport demands excellent fitness: players require aerobic stamina, agility, strength, speed, and precision. It is also a technical sport, requiring good motor coordination and the development of sophisticated racquet movements.
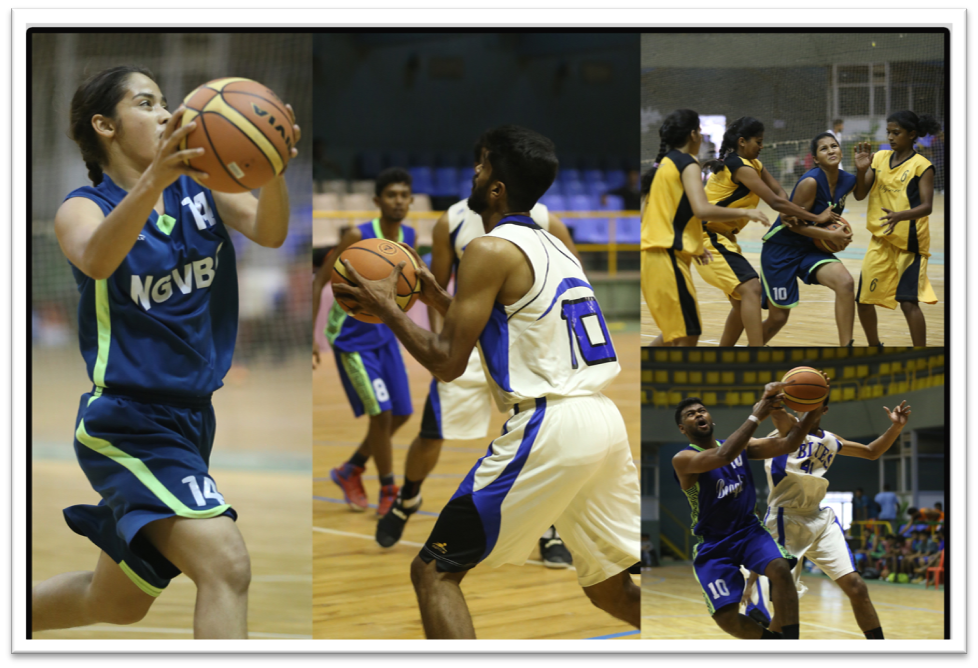

Basketball is a sport that is played by two teams of five players on a rectangular court. The objective is to shoot a ball through a hoop 18 inches (46 cm) in diameter and mounted at a height of 10 feet (3.048 m) to backboards at each end of the court. Basketball courts come in different sizes and colors. Under International Basketball Federation (FIBA) rules, the court is minutely smaller, measuring exactly 28 by 15 metres (92 by 49 ft). Usually match is game is 4 quarters of 12 minutes each, for a total of 48 minutes. The team with more points at the end of the game wins. Basketball was introduced in Olympics in 1936. It was first incorporated into the Asian Games in 1951. The United States is by far the most successful country in Olympic basketball, with United States men's teams having won 15 of 18 tournaments which they participated in, including seven successive titles from 1936 to 1968.
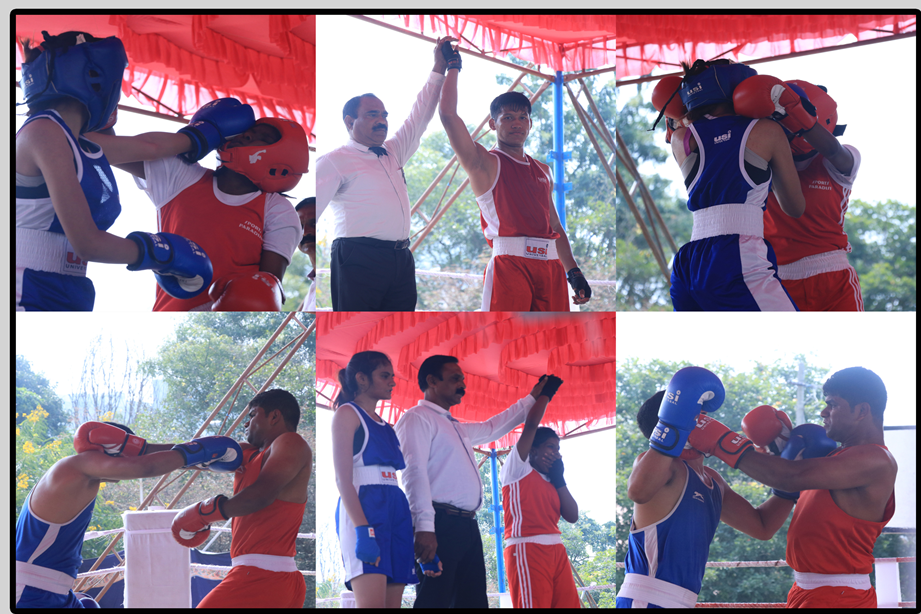

Boxing is a combat sport in which two people, usually wearing protective gloves, throw punches at each other for a predetermined set of time in a boxing ring. Boxing is supervised by a referee over a series of one- to three-minute intervals called rounds.
While humans have fought in hand-to-hand combat since before the dawn of history, boxing as an organized sport may have its origin in the ancient Greeks as an Olympic game in 688 BC. Boxing evolved from 16th- and 18th-century prizefights, largely in Great Britain, to the forerunner of modern boxing in the mid-19th century with the 1867 introduction of the Marquess of Queensberry Rules. The earliest known depiction of boxing comes from a Sumerian relief in Iraq from the 3rd millennium BCE.[2] Later depictions from the 2nd millennium BC are found in reliefs from the Mesopotamian nations of Assyria and Babylonia, and in Hittite art from Asia Minor.
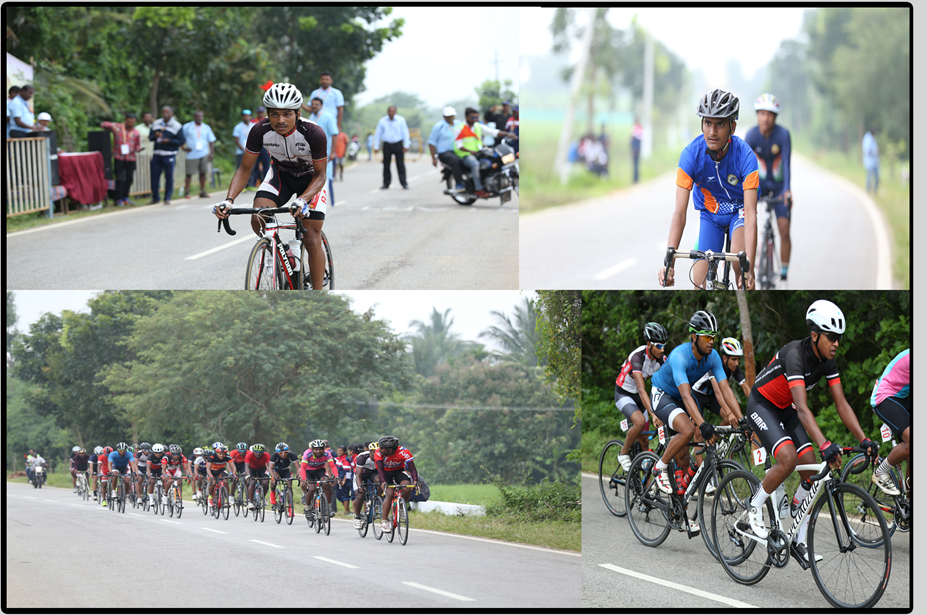

Cycling, also called bicycling or biking, is the use of bicycles for transport, recreation, exercise or sport. Persons engaged in cycling are referred to as "cyclists", "bikers" or less commonly, as "bicyclists". Apart from two-wheeled bicycles, "cycling" also includes the riding of unicycles, tricycles, quadracycles, recumbent and similar human-powered vehicles (HPVs).
Bicycles were introduced in the 19th century and now number approximately one billion worldwide. They are the principal means of transportation in many parts of the world.
Bicycles provide numerous benefits in comparison with motor vehicles, including the sustained physical exercise involved in cycling, easier parking, increased maneuverability, and access to roads, bike paths and rural trails. Cycling also offers a reduced consumption of fossil fuels, less air or noise pollution, and much reduced traffic congestion. These lead to less financial cost to the user as well as to society at large (negligible damage to roads, less road area required). By fitting bicycle racks on the front of buses, transit agencies can significantly increase the areas they can serve.
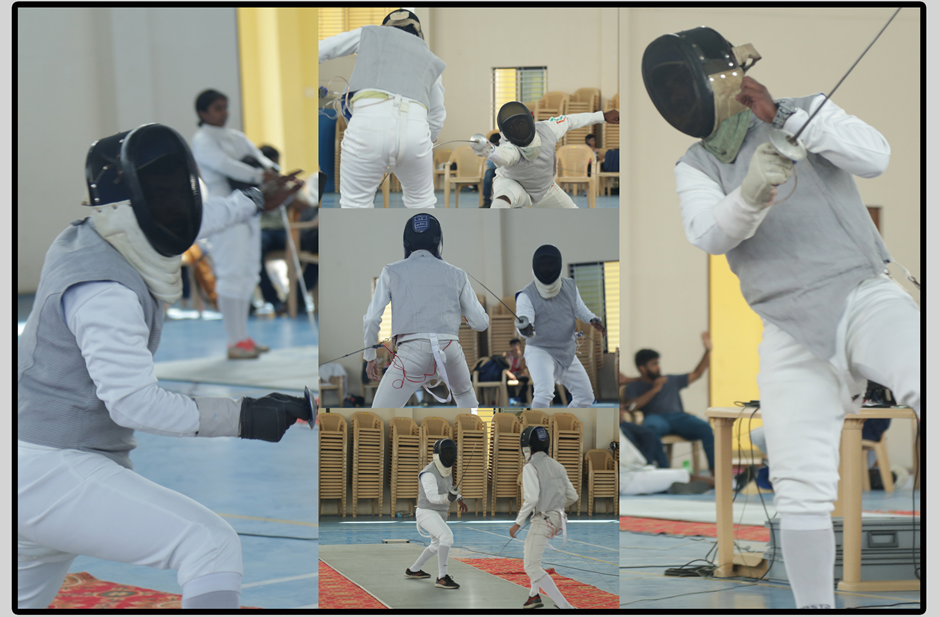

Fencing is a sport in which two competitors fight using 'rapier-style' swords, called the foil. here are three forms of modern fencing, each uses a different kind of weapon and has different rules, this way the sport itself is divided into three competitive scenes: foil and sabre. Most competitive fencers choose to specialize in one weapon only. Competitive fencing is one of the five activities which have been featured in every modern Olympic Games.
Fencing is governed by Fédération Internationale d'Escrime (FIE). Today, its head office is in Lausanne, Switzerland. The FIE is composed of 145 national federations, each of which is recognised by its state Olympic Committee as the sole representative of Olympic-style fencing in that country. The FIE maintains the current rules used by FIE sanctioned international events, including world cups, world championships and the Olympic Games. The FIE handles proposals to change the rules the first year after an Olympic year in the annual congress. The US Fencing Association has slightly different rules, but usually adheres to FIE standards.
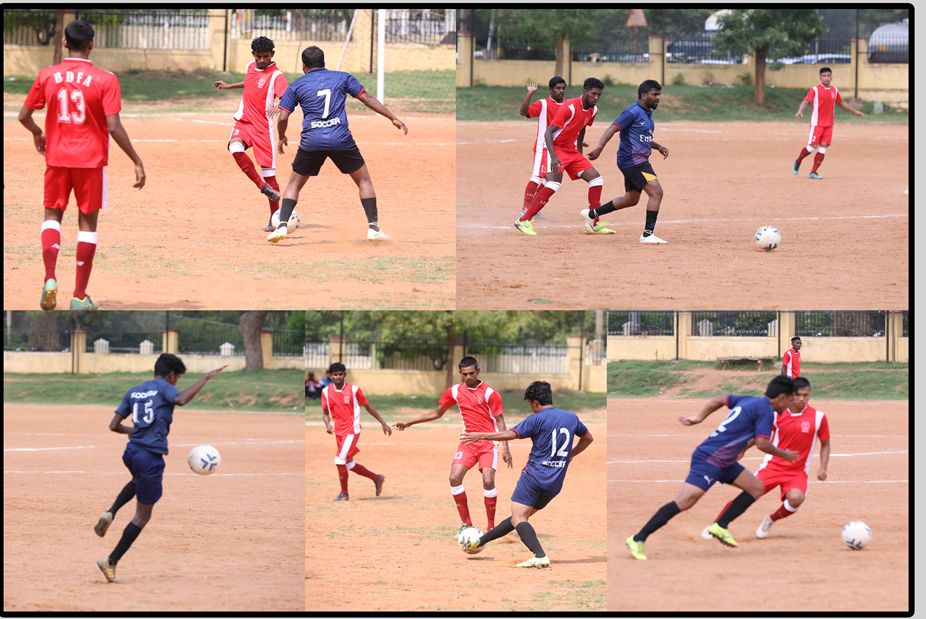

Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball with a foot to score a goal. Unqualified, the word football is understood to refer to whichever form of football is the most popular in the regional context in which the word appears. The different variations of football are known as football codes.
Various forms of football can be identified in history, often as popular peasant games. Contemporary codes of football can be traced back to the codification of these games at English public schools during the nineteenth century. The expanse of the British Empire allowed these rules of football to spread to areas of British influence outside the directly controlled Empire. By the end of the nineteenth century, distinct regional codes were already developing: Gaelic football, for example, deliberately incorporated the rules of local traditional football games in order to maintain their heritage. In 1888, The Football League was founded in England, becoming the first of many professional football competitions.
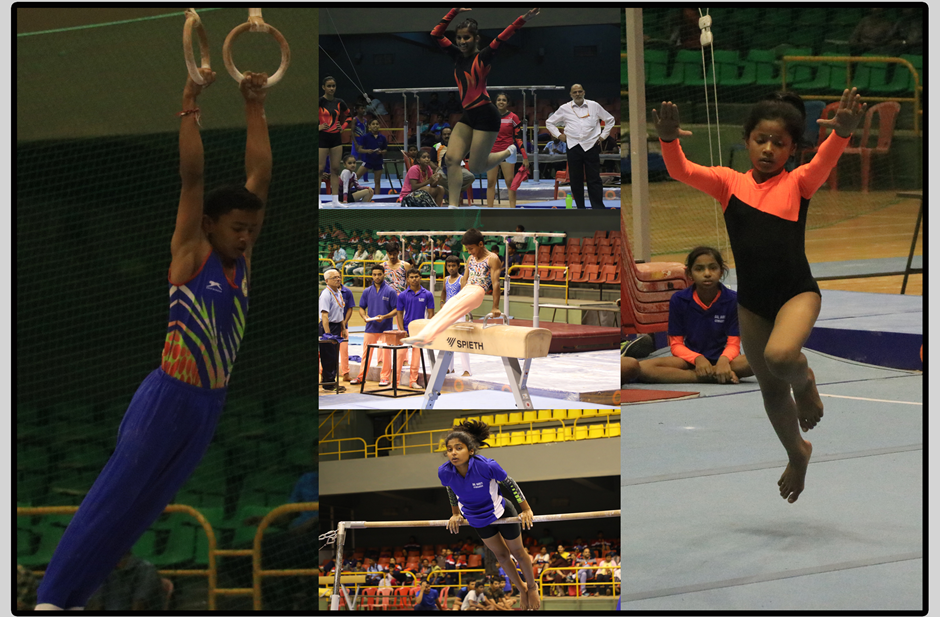
Gymnastics is a sport practiced by men and women that requires balance, strength, flexibility, agility, coordination, endurance and control. The movements involved in gymnastics contribute to the development of the arms, legs, shoulders, back, chest and abdominal muscle groups. Alertness, precision, daring, self-confidence and self-discipline are mental traits that can also be developed through gymnastics.
Most forms of competitive gymnastics events are governed by the Fédération Internationale de Gymnastique (FIG). Each country has its own national governing body (BIW) affiliated to FIG. Competitive artistic gymnastics is the best known of the gymnastic events. It typically involves the women's events of vault, uneven bars, balance beam and floor exercise. Men's events are floor exercise, pommel horse, still rings, vault, parallel bars and horizontal bar. Other FIG disciplines include rhythmic gymnastics, trampolining and tumbling, acrobatic gymnastics and aerobic gymnastics. Disciplines not currently recognized by FIG include wheel gymnastics, aesthetic group gymnastics, men's rhythmic gymnastics and TeamGym.
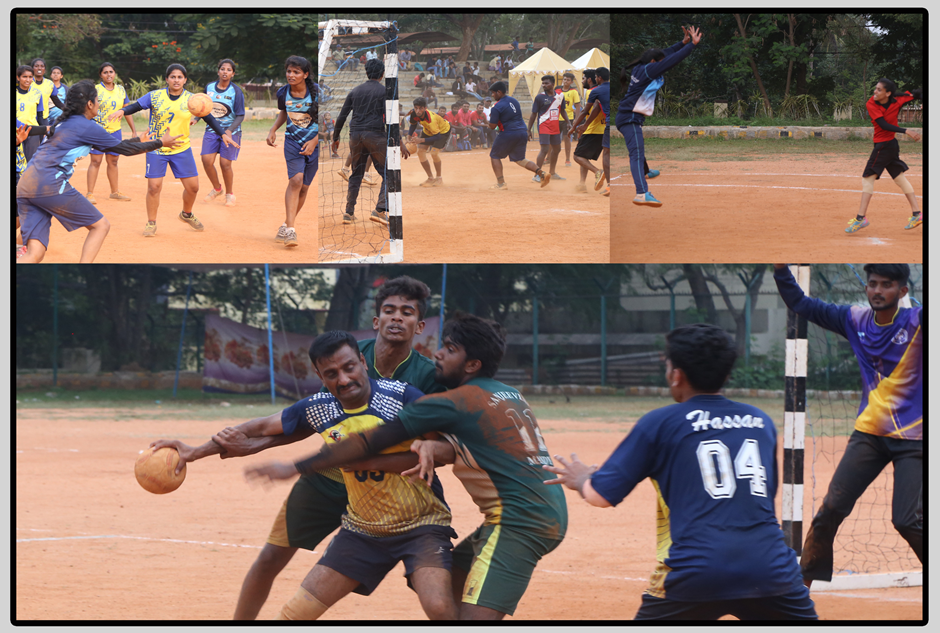

Handball is also known as team handball or Olympic handball. It is a team sport in which two teams of seven players each (six outfield players and a goalkeeper) pass a ball using their hands with the aim of throwing it into the goal of the other team. A standard match consists of two periods of 30 minutes, and the team that scores more goals wins.
Modern handball is played on a court 40 by 20 metres (131 by 66 ft), with a goal in the middle of each end. The goals are surrounded by a 6-meter (20 ft) zone where only the defending goalkeeper is allowed; goals must be scored by throwing the ball from outside the zone or while "diving" into it. The sport is usually played indoors, but outdoor variants exist in the forms of field handball and Czech handball (which were more common in the past) and beach handball. The game is fast and high-scoring: professional teams now typically score between 20 and 35 goals each, though lower scores were not uncommon until a few decades ago. Body contact is permitted by the defenders trying to stop the attackers from approaching the goal.
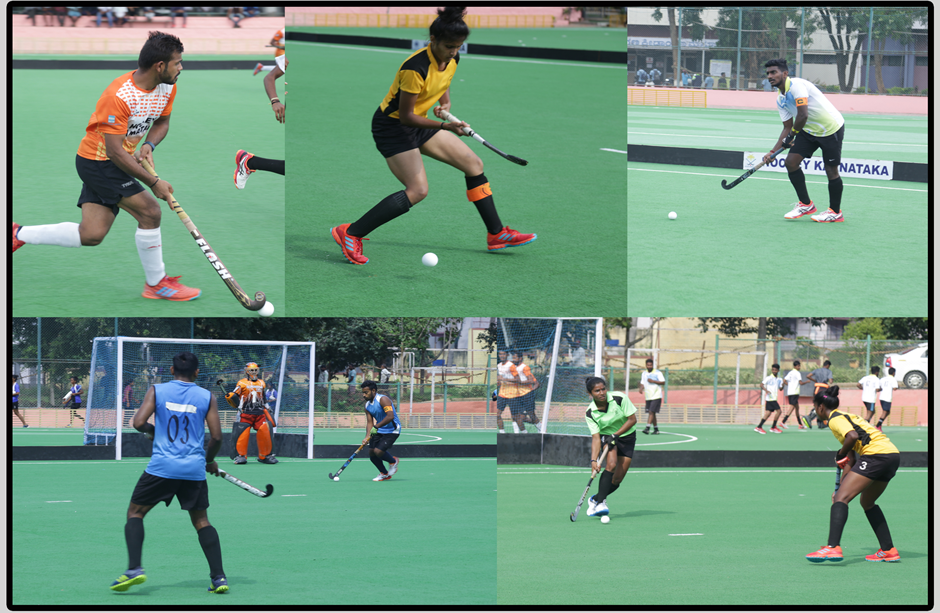

Hockey is a sport in which two teams play against each other by trying to maneuver a ball or a puck into the opponent's goal using a hockey stick. There are many types of hockey such as bandy, field hockey and ice hockey. Often one variation of the sport, such as field hockey or ice hockey, will predominate in a certain area and be known simply as "hockey".
The word hockey itself is of unknown origin. One supposition is that it is a derivative of hoquet, a Middle French word for a shepherd's stave. The curved, or "hooked" ends of the sticks used for hockey would indeed have resembled these staves. Another supposition derives from the known use of cork bungs, (stoppers) in place of wooden balls to play the game. The stoppers came from barrels containing "hock" ale, also called "hocky". Games played with curved sticks and a ball can be found in the histories of many cultures.
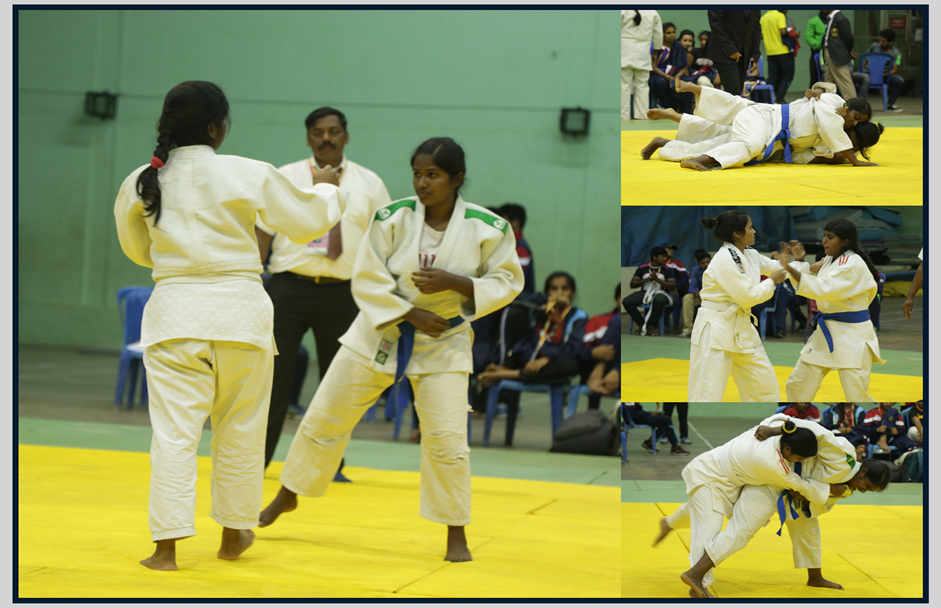

It is generally categorized as a Modern martial art which later evolved into combat and Olympic sport. Its most prominent feature is its competitive element, where the objective is to either throw or takedown an opponent to the ground, immobilize or otherwise subdue an opponent with a pin, or force an opponent to submit with a Joint lock or a Choke. Strikes and thrusts by hands and feet as well as weapons defences are a part of judo, but only in pre-arranged forms and are not allowed in judo competition or free practice. A judo practitioner is called a judoka. Judo became an Olympic sport for men in the 1964 Games in Tokyo. The women's event was introduced at the Olympics in 1988 as a demonstration event, and an official medal event in 1992. Judo was first incorporated into the Asian Games in 1986.
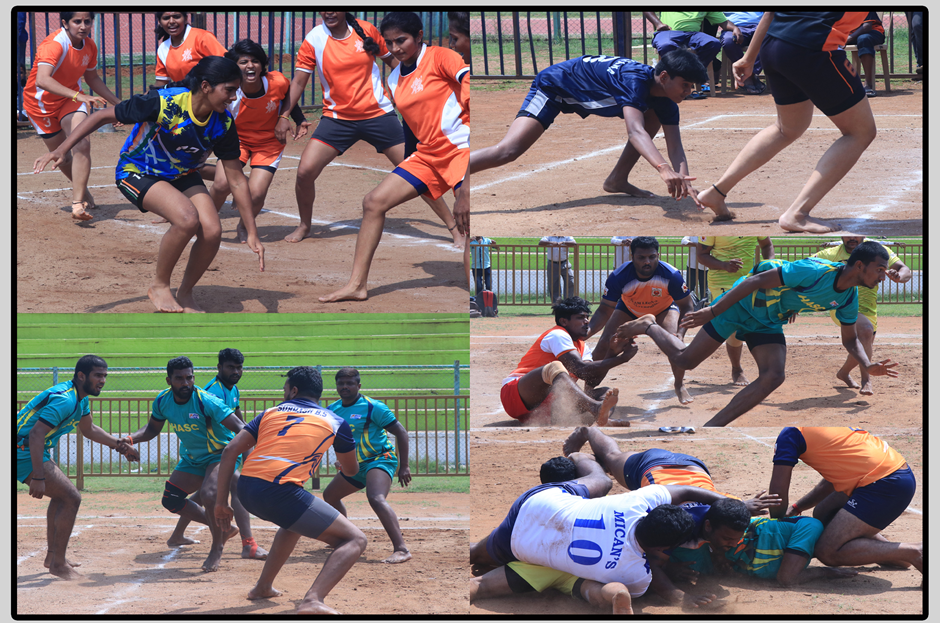

Kabaddi is a contact team sport whose origination is not traceable. It is popular in South Asia and is the state game of the Indian states of Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Haryana, Karnataka, Maharashtra, Punjab and Telangana. Kabaddi is played between two teams of seven players; the object of the game is for a single player on offence—referred to as a "raider"—to run into the opposing team's half of a court, tag out as many of their defenders as possible, and return to their own half of the court—all without being tackled by the defenders.
The game is known by its regional names in different parts of the subcontinent, such as Kabaddi or Chedugudu in Andhra Pradesh, Kabaddi in Kerala and Telangana, Hadudu in Bangladesh, Bhavatik in Maldives, Kauddi or Kabaddi in the Punjab region, Hu-Tu-Tu in Western India and Hu-Do-Do in Eastern India and chadakudu in South India.
Kabaddi, originated in ancient Tamil region, which is predominantly present day Tamil Nadu and parts of other South Indian states. Tamil empire spread this game to South East Asia during their sea trade. The word Kabaddi might have been derived from the Tamil word "kai-pidi" meaning "to hold hands".
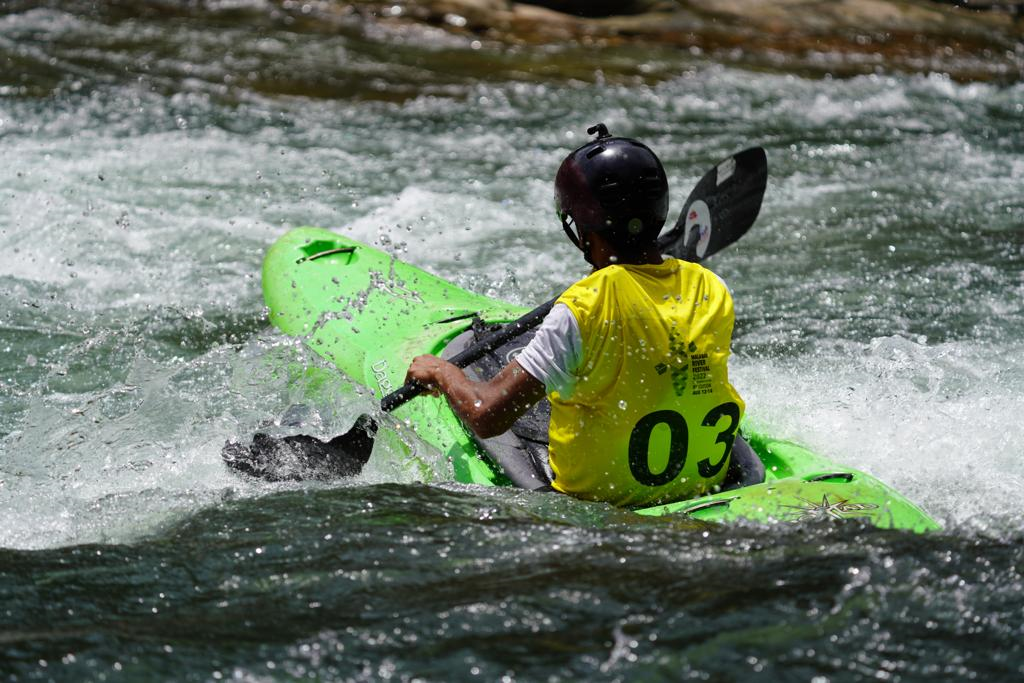

Canoe – this is an open vessel and the paddler kneels and uses a single-bladed paddle to propel the boat forward.
Kayak – this is an enclosed vessel and the paddler is seated and uses a double-bladed paddle pulling the blade through the water on alternate sides to move forward.
Both the Canoe and Kayak are raced from club to Olympic level, with variations in the boat design depending on type of water and discipline – sprint & slalom.
Sprint - sprint takes place on a flatwater course and races are contested by two types of boat, canoe (C) and kayak (K). For each of the disciplines there are multiple types of boats; canoe sprint races are categorised based on the type of boat, number of people in the boat, the gender of the competitors, and the distance of the race.
Slalom - there are three different types of boat the Kayak Singles (K1), Canoe Singles (C1) and Canoe Doubles (C2)
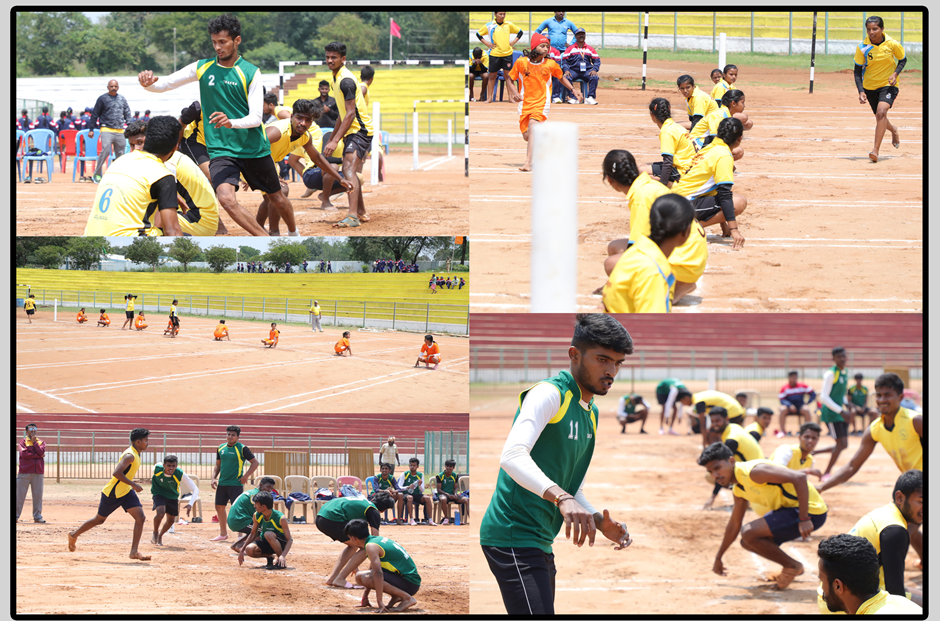

Kho kho is a popular tag sport from India. It is played by teams of twelve nominated players out of fifteen, of which nine enter the field, who try to avoid being touched by members of the opposing team. It is one of the two most popular traditional tag games of the South Asia, the other being Kabaddi. Apart from South Asia, it is also played by the Indian community in South Africa.
The word kho seems to be derived from the Sanskrit verb root syu- meaning "get up go".
The 1st Asian Championship was held at Kolkata in 1996 and the second championship at Dhaka, Bangladesh. India, Sri Lanka, Pakistan, Nepal, Japan, Thailand and Bangladesh were participants of this championship.
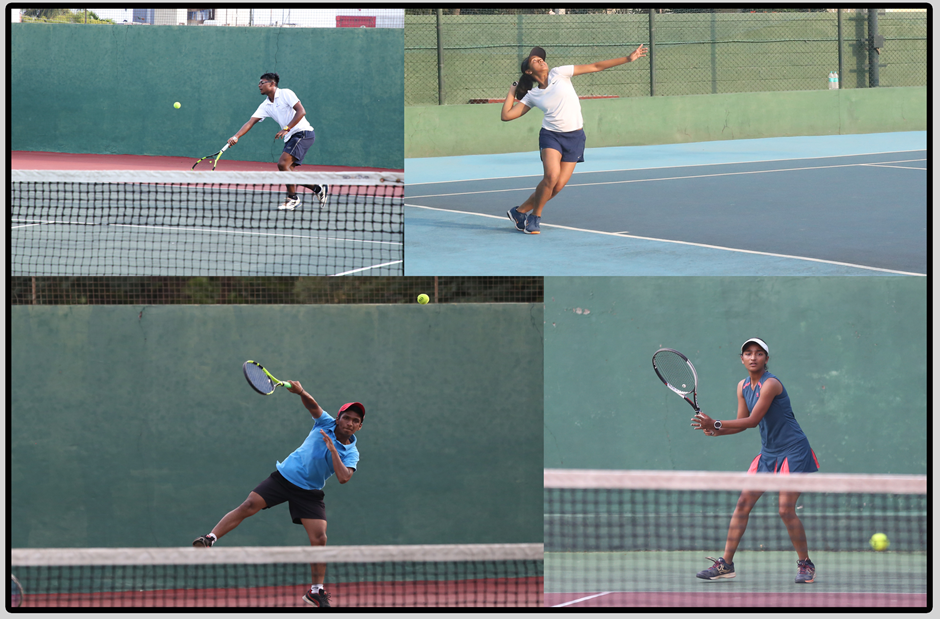

Tennis is a racket sport that can be played individually against a single opponent (singles) or between two teams of two players each (doubles). Each player uses a tennis racket that is strung with cord to strike a hollow rubber ball covered with felt over or around a net and into the opponent's court. The object of the game is to play the ball in such a way that the opponent is not able to play a valid return.
Tennis is an Olympic sport and is played at all levels of society and at all ages. The sport can be played by anyone who can hold a racket, including wheelchair users. The modern game of tennis originated in Birmingham, England, in the late 19th century as lawn tennis. It had close connections both to various field (lawn) games such as croquet and bowls as well as to the older racket sport today called real tennis. During most of the 19th century, in fact, the term tennis referred to real tennis, not lawn tennis: for example, in Disraeli's novel Sybil (1845), Lord Eugene De Vere announces that he will "go down to Hampton Court and play tennis.
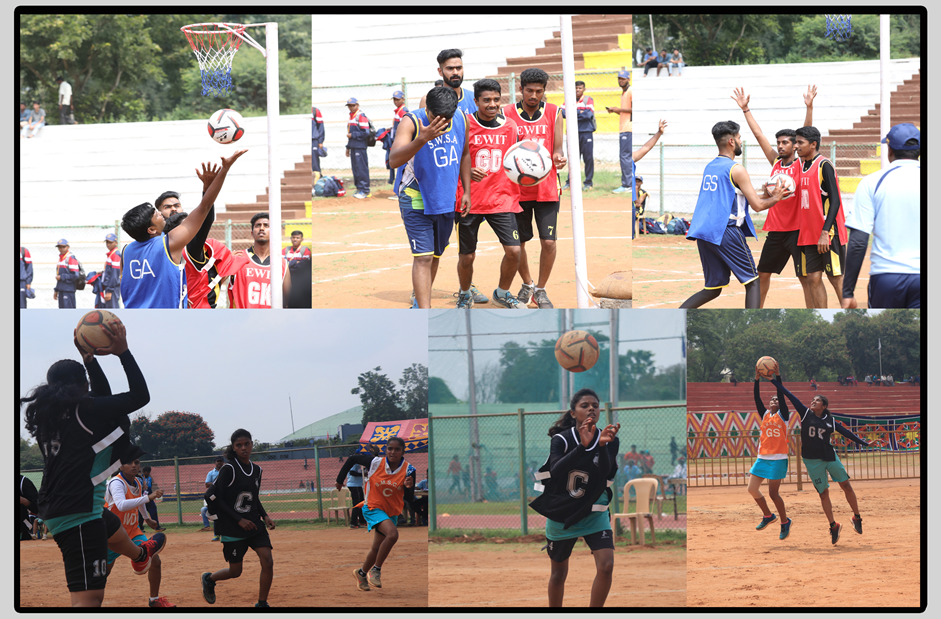

Netball is a ball sport played by two teams of seven players. Its development, derived from early versions of basketball, began in England in the 1890s. By 1960, international playing rules had been standardised for the game, and the International Federation of Netball and Women's Basketball (later renamed the International Netball Federation (INF)) was formed. As of 2011, the INF comprises more than 60 national teams organized into five global regions.
Netball is most popular in Commonwealth nations, specifically in schools, and is predominantly played by women. According to the INF, netball is played by more than 20 million people in more than 80 countries. Major domestic leagues in the sport include the Netball Superleague in Great Britain, Suncorp Super Netball in Australia and the ANZ Premiership in New Zealand. Four major competitions take place internationally: the quadrennial World Netball Championships, the Commonwealth Games, and the yearly Quad Series and Fast5 Series. In 1995, netball became an International Olympic Committee recognised sport, but it has not been played at the Olympics.
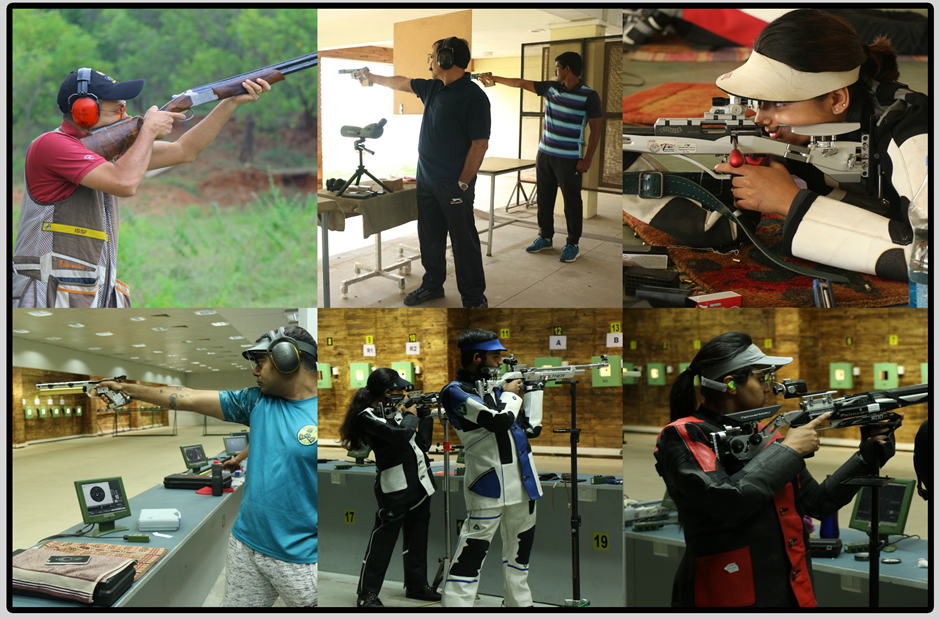

Rifle Shooting sports is a collective group of competitive and recreational sporting activities involving proficiency tests of accuracy, precision and speed in using various types of ranged weapons, mainly referring to man-portable guns (firearms and airguns, in forms such as handguns, rifles and shotguns and bows/crossbows. Shooting sports may involve both team and individual competition, and team performance is usually assessed by summing the scores of the individual team members.
The National Rifle Association of the United Kingdom (NRA) was founded in 1860 to raise the funds for an annual national rifle meeting "for the encouragement of Volunteer Rifle Corps and the promotion of Rifle-shooting throughout Great Britain".
For similar reasons, concerned over poor marksmanship during the American Civil War, veteran Union officers Col. William C. Church and Gen. George Wingate formed the National Rifle Association of America in 1871 for the purpose of promoting and encouraging rifle shooting on a "scientific" basis. In 1872, with financial help from New York state, a site on Long Island, the Creed Farm, was purchased for the purpose of building a rifle range.
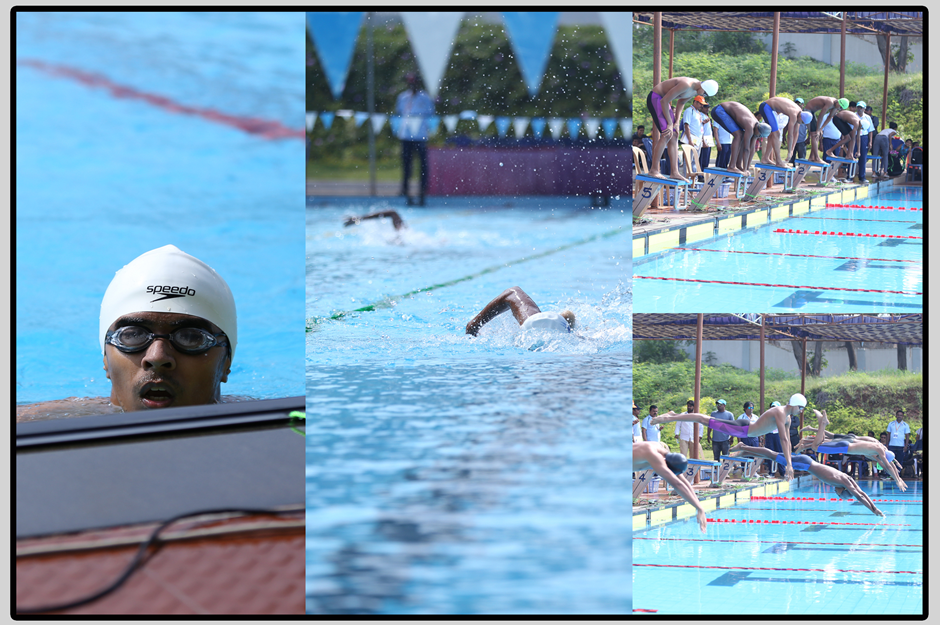
Swimming is the self-propulsion of a person through water or another liquid, usually for recreation, sport, exercise, or survival. Locomotion is achieved through coordinated movement of the limbs, the body, or both. Humans can hold their breath underwater and undertake rudimentary locomotive swimming within weeks of birth, as an evolutionary response.
Swimming is consistently among top public recreational activities and in some countries, swimming lessons are a compulsory part of the educational curriculum. As a formalized sport, swimming features in a range of local, national, and international competitions, including every modern summer Olympics. Swimming relies on the natural buoyancy of the human body. On average, the body has a relative density of 0.98 compared to water, which causes the body to float.
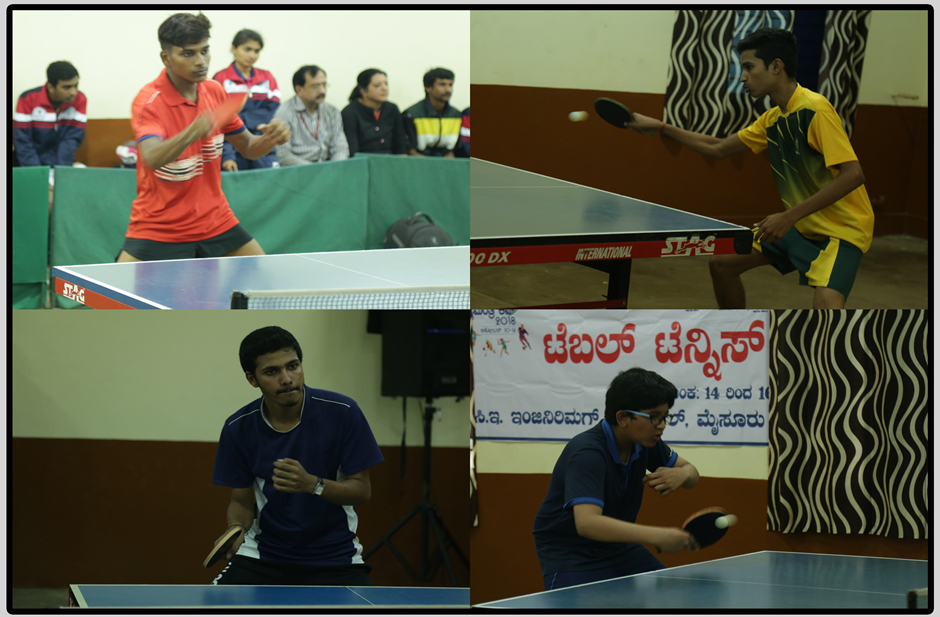

Table tennis, also known as ping pong, is a sport in which two or four players hit a lightweight ball back and forth across a table using small bats. The game takes place on a hard table divided by a net. Except for the initial serve, the rules are generally as follows: players must allow a ball played toward them to bounce one time on their side of the table, and must return it so that it bounces on the opposite side at least once.
Table tennis is governed by the worldwide organization International Table Tennis Federation (ITTF), founded in 1926. ITTF currently includes 226 member associations. The table tennis official rules are specified in the ITTF handbook. Table tennis has been an Olympic sport since 1988,[5] with several event categories. From 1988 until 2004, these were men's singles, women's singles, men's doubles and women's doubles. Since 2008, a team event has been played instead of the doubles.
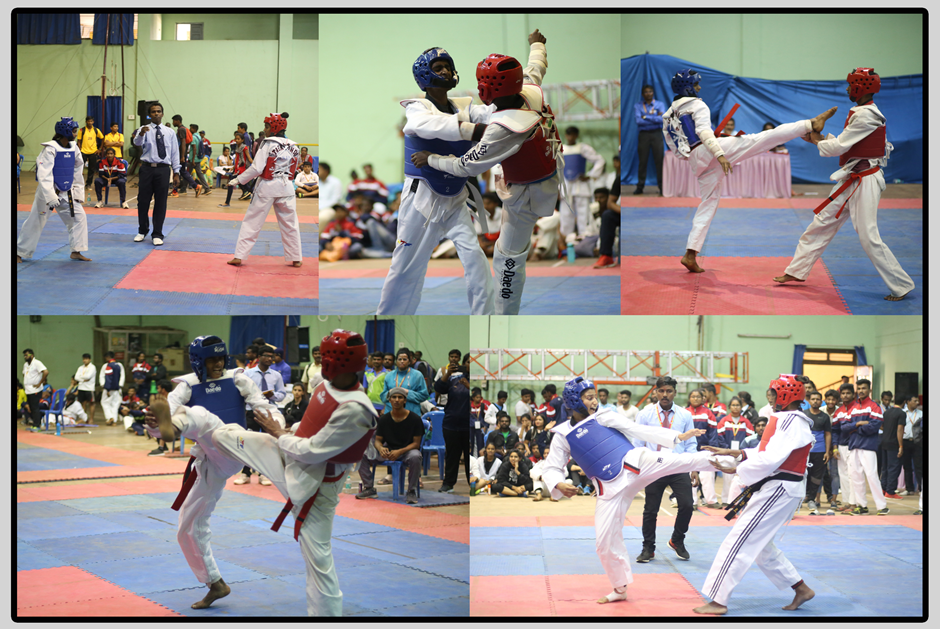

Taekwondo is a Korean martial art. Taekwondo is loosely translated as .the way of the foot and fist. but some translate it as, .the art of kicking and punching., Taekwondo's popularity is a result of evolution of martial arts. Taekwondo was developed during the 1940.s and 1950.s by various martial artists by incorporating elements of Karate and Chinese Martial Arts with indigenous Korean martial arts. It combines combat techniques, self-defence, sport, exercise, meditation and philosophy. Modern Taekwondo tends to emphasize control and self-defence. The art in general emphasizes kicks thrown from a mobile stance, employing the leg's greater reach and power. Taekwondo training generally includes a system of blocks, kicks, punches, and open-handed strikes and may also include various take-downs or sweeps, throws, and joint locks. Taekwondo was incorporated into the Asian Games in 1986. It became a full medal sport at the 2000 Summer Olympics in Sydney, Australia.
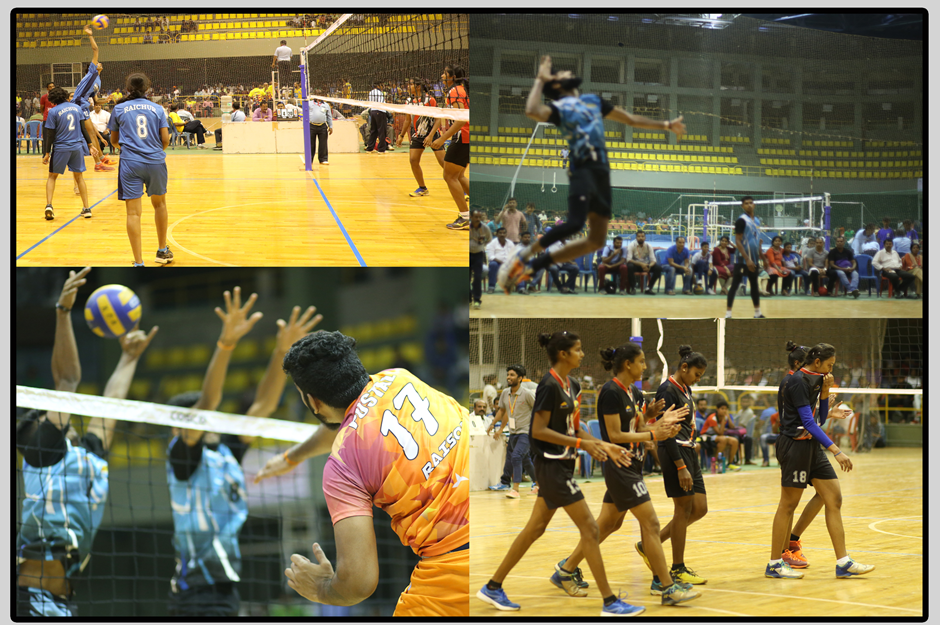

Volleyball is a team sport in which two teams of six players are separated by a net. Each team tries to score points by grounding a ball on the other team's court under organized rules. It has been a part of the official program of the Summer Olympic Games since 1964. Typically, the first two touches are used to set up for an attack, an attempt to direct the ball back over the net in such a way that the serving team is unable to prevent it from being grounded in their court.
The team may touch the ball up to 3 times but individual players may not touch the ball twice consecutively. Typically, the first two touches are used to set up for an attack, an attempt to direct the ball back over the net in such a way that the serving team is unable to prevent it from being grounded in their court. The rally continues, with each team allowed as many as three consecutive touches, until either a team makes a kill, grounding the ball on the opponent's court and winning the rally; or a team commits a fault and loses the rally. The team that wins the rally is awarded a point, and serves the ball to start the next rally.
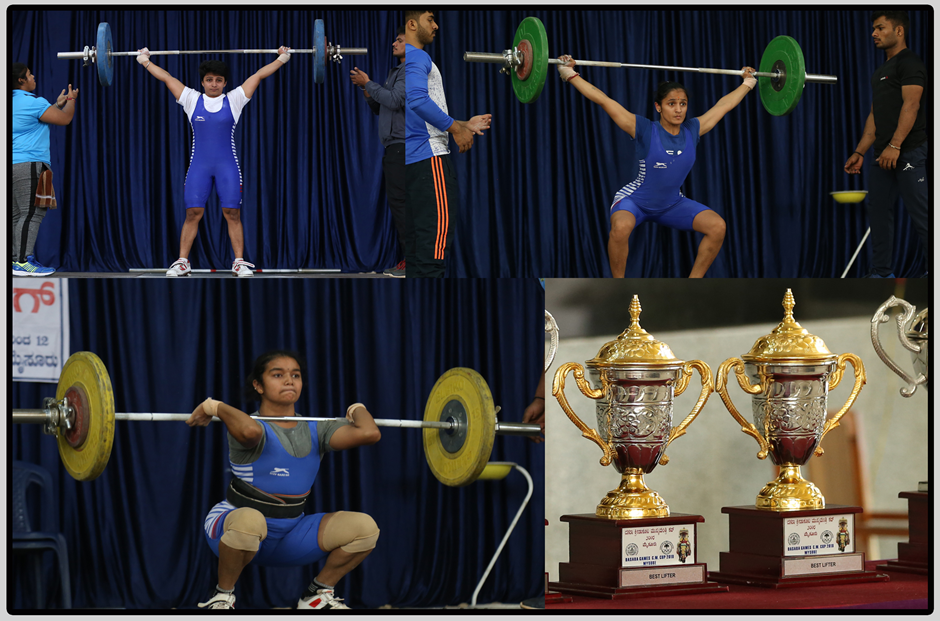

Weightlifting, also called Olympic-style weightlifting, or Olympic weightlifting, is an athletic discipline in the modern Olympic programme in which the athlete attempts a maximum-weight single lift of a barbell loaded with weight plates. Each weightlifter receives three attempts in each, and the combined total of the highest two successful lifts determines the overall result within a bodyweight category.
A lifter who fails to complete at least one successful snatch and one successful clean and jerk also fails to total, and therefore receives an "incomplete" entry for the competition. The clean and press was once a competition lift, but was discontinued due to difficulties in judging proper form.
While there are relatively few competitive Olympic weightlifters, the lifts performed in the sport of weightlifting, and in particular their component lifts (e.g. squats, deadlifts, cleans), are commonly used by elite athletes in other sports to train for both explosive and functional strength.
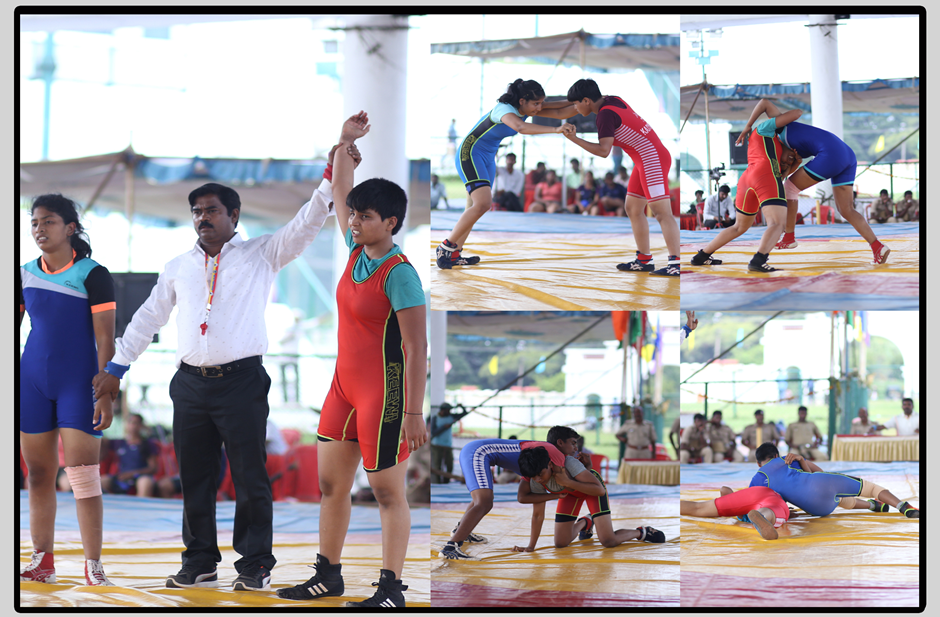

Wrestling is a combat sport involving grappling type techniques such as clinch fighting, throws and takedowns, joint locks, pins and other grappling holds. The sport can either be theatrical for entertainment, or genuinely competitive. A wrestling bout is a physical competition, between two (occasionally more) competitors or sparring partners, who attempt to gain and maintain a superior position. Wrestling techniques have been incorporated into other martial arts as well as military hand-to-hand combat systems.
Wrestling represents one of the oldest forms of combat. The origins of wrestling go back 15,000 years through cave drawings in France. Babylonian and Egyptian reliefs show wrestlers using most of the holds known in the present-day sport. Literary references to it occur as early as the Old Testament and the ancient Indian Vedas.
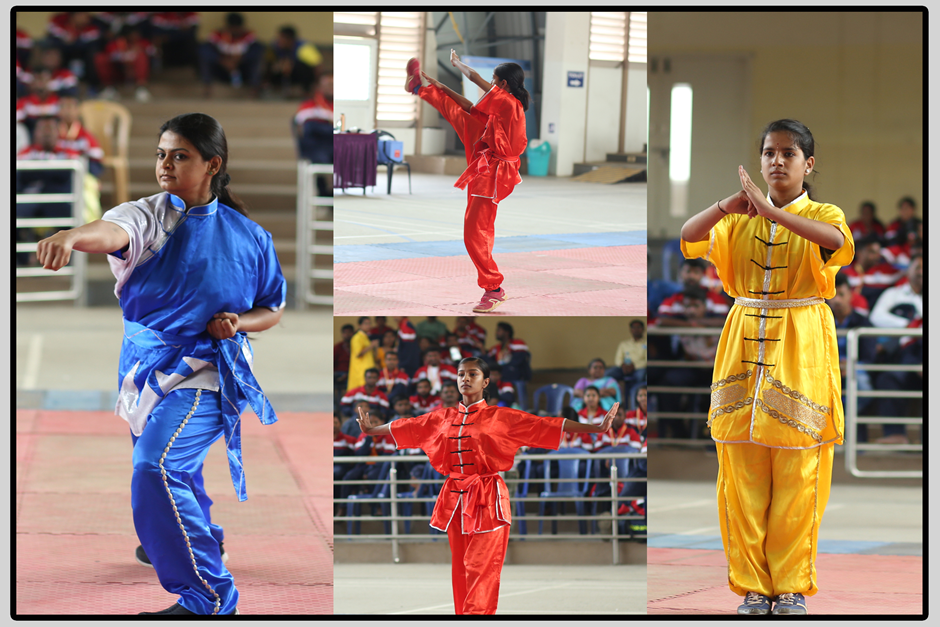

Wushu or kungfu is a martial art and a full-contact sport. It was developed in China after 1949. Competitive wushu is composed of two disciplines that is taolu and sanda. The forms comprise basic movements (stances, kicks, punches, balances, jumps, sweeps, and throws) based on aggregate categories of traditional Chinese martial art styles, and can be changed for competitions to highlight one's strengths. In 1958, the government established the All-China Wushu Association as an umbrella organization to regulate martial arts training. The Chinese State Commission for Physical Culture and Sports took the lead in creating standardized forms for most of the major arts. During this period, a national Wushu system that included standard forms, teaching curriculum, and instructor grading was established. Wushu was introduced at both the high school and university level.

























